A remote desktop program called TeamViewer enables users to access computers from a distance. Although largely secure, inappropriate use may cause issues.
TeamViewer is useful for reliable remote collaboration and assistance when used properly. Users must follow the rules and get permission to ensure its ethical and legal use.
We intend to inform you if the misuse or unauthorized access can be tracked, perhaps resulting in legal repercussions. Read on.
Can You be Caught Using TeamViewer?
TeamViewer enables users to connect to and manage computers from a distance, enabling remote collaboration and support.

It is possible to get caught using TeamViewer for illegal activities. Although TeamViewer is a reliable remote desktop access and support tool, using it improperly might have severe repercussions.
IP addresses, activity logs, and digital footprints are just a few ways someone might be identified if they break into someone else’s computer or use it for harmful purposes.
Cybersecurity professionals, law enforcement authorities, or anyone who is harmed can look into and determine where suspicious actions started.
Users should only use TeamViewer responsibly and with the appropriate authorization to stay out of problems.
Can TeamViewer be tracked?
While TeamViewer encrypts and securely stores these logs, misuse or suspicious activity may warrant a request for access from law enforcement or other authorized parties with the appropriate legal procedures.
Activities performed with TeamViewer can be somewhat tracked. TeamViewer records connection information such as IP addresses, timestamps, and session lengths for security and debugging purposes.
In addition, some security professionals have expressed concern about potential flaws in TeamViewer that attackers can exploit.
Therefore, it is essential to follow standard security practices and keep the TeamViewer software and the underlying operating system updated to reduce any possible dangers.
How Students Use TeamViewer to Cheat
Remote Exam Taking
Students can use TeamViewer to let another person—often someone more qualified—take an exam on their behalf.
Without the test proctor’s knowledge, the remote user gains access to the student’s computer and can supply solutions or finish tasks during the test.
Copying Answers
Students use TeamViewer to share their computer screens with others during examinations or assessments so they can copy answers.
The remote users can see the test questions and give the students taking the test immediate responses.
When you copy the answers, the learner can cheat using this technique without covertly accessing outside resources.
Such behaviors undermine the validity of evaluations and go against the rules of academic integrity.
Collaborative Cheating
Students who use TeamViewer or similar remote desktop programs to collaborate on coursework or examinations without real participation engage in collaborative cheating.
They might use each other’s computers to share solutions or answers, which would inaccurately represent their own efforts.
In addition to undermining the standards of academic integrity, this type of cheating also violates them.
Universities strictly forbid such behavior and penalize students caught participating in collaborative cheating since it undermines the authenticity and fairness of exams.
How Universities Detect TeamViewer
1. Network Monitoring
The process of studying and examining network traffic to spot patterns, anomalies, and potential security risks is known as network monitoring.
Universities utilize network monitoring technologies to protect their networks’ security and ensure that their acceptable use guidelines are being followed.
When one watches network traffic, administrators can spot unapproved programs like TeamViewer, which may be used for academic dishonesty or unlawful access to resources.
Thanks to this proactive strategy, universities can take the essential steps to maintain a safe and equitable learning environment while encouraging responsible use of their network resources.
2. Firewall Rules
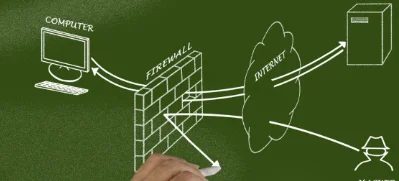
To manage incoming and outgoing traffic, network devices like routers and firewalls employ a set of policies called firewall rules. Universities can use firewall rules to deny or limit access to particular programs, such as TeamViewer.
Universities can enforce their acceptable usage regulations and avoid potential software misuse by setting up rules that forbid TeamViewer-related traffic from traveling via the network.
Even so, this safeguard assists in maintaining network security, safeguarding private data, and fostering an atmosphere favorable to appropriate academic activity.
3. Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
A network monitoring technique called Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) looks at the content of data packets as they go through a network.
Universities may use DPI to examine the network traffic’s payload and spot particular patterns or TeamViewer-related signatures.
Administrators can enforce network restrictions by employing DPI to find applications being used without authorization.
DPI makes it possible to analyze network traffic more thoroughly and precisely, assisting institutions in maintaining a safe and impartial learning environment and guarding against possible security breaches.
4. Endpoint Security Software
Endpoint security software is connected to the university’s network to safeguard them from various dangers, such as malware like TeamViewer and other illegal or dangerous software.
To ensure that only approved software is used, the program can identify such apps and stop them from being installed or run.
Endpoint security adds another line of defense against potential security breaches or academic misconduct in the university’s computing environment by assisting in detecting and blocking suspicious activity.
5. User Reporting and Monitoring
Encourage staff and students to report any unlawful or suspected use of software like TeamViewer as part of user reporting and monitoring.
Universities may have procedures for anonymous reporting or employees assigned to handle such allegations.
Monitoring user activity on the network also makes it easier to spot odd trends or unwanted access attempts.
Administrators can promptly respond to possible security risks, enforce policies, and maintain a secure and moral academic environment by actively involving the university community in reporting and monitoring actions.
6. Application Whitelisting/Blacklisting
Universities utilize security methods like application whitelisting and blacklisting to manage the software permitted on their networks. Whitelisting restricts access to only approved programs, such as university-approved software.
In contrast, blacklisting prohibits particular apps, such as TeamViewer, or other potentially unauthorized or harmful software.
Universities can reduce the risk of security breaches and academic dishonesty and ensure that only permitted and secure software is used within their network environment by using these lists to block the installation or execution of forbidden programs.
